Encryption for EveryBody - Encryption Let me Count the Ways!
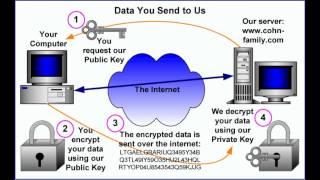
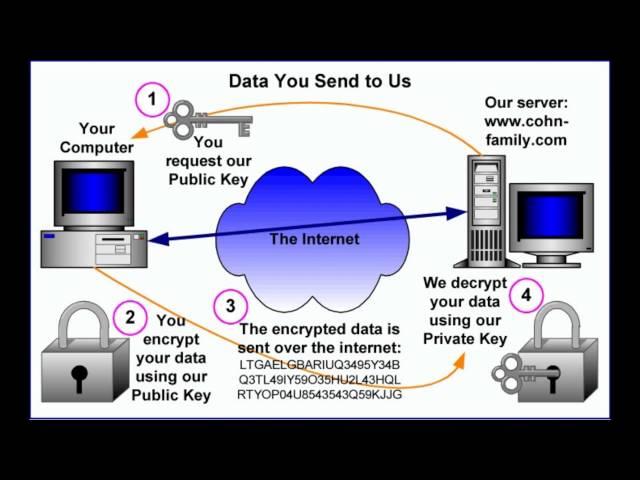
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding messages (or information) in such a way that eavesdroppers or hackers cannot read it, but that authorized parties can.[1]:374 In an encryption scheme, the message or information (referred to as plaintext) is encrypted using an encryption algorithm, turning it into an unreadable ciphertext (ibid.). This is usually done with the use of an encryption key, which specifies how the message is to be encoded. Any adversary that can see the ciphertext should not be able to determine anything about the original message. An authorized party, however, is able to decode the ciphertext using a decryption algorithm, that usually requires a secret decryption key, that adversaries do not have access to. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually needs a key-generation algorithm to randomly produce keys.
There are two basic types of encryption schemes: Symmetric-key and public-key encryption.[1]:375-376 In symmetric-key schemes, the encryption and decryption keys are the same. Thus communicating parties must agree on a secret key before they wish to communicate. In public-key schemes, the encryption key is published for anyone to use and encrypt messages. However, only the receiving party has access to the decryption key and is capable of reading the encrypted messages.[2] Public-key encryption is a relatively recent invention: historically, all encryption schemes have been symmetric-key (also called private-key) schemes.[1]:478
Encryption has long been used by militaries and governments to facilitate secret communication. It is now commonly used in protecting information within many kinds of civilian systems. For example, the Computer Security Institute reported that in 2007, 71% of companies surveyed utilized encryption for some of their data in transit, and 53% utilized encryption for some of their data in storage.[3] Encryption can be used to protect data "at rest", such as files on computers and storage devices (e.g. USB flash drives). In recent years there have been numerous reports of confidential data such as customers' personal records being exposed through loss or theft of laptops or backup drives. Encrypting such files at rest helps protect them should physical security measures fail. Digital rights management systems which prevent unauthorized use or reproduction of copyrighted material and protect software against reverse engineering (see also copy protection) is another somewhat different example of using encryption on data at rest.
There are two basic types of encryption schemes: Symmetric-key and public-key encryption.[1]:375-376 In symmetric-key schemes, the encryption and decryption keys are the same. Thus communicating parties must agree on a secret key before they wish to communicate. In public-key schemes, the encryption key is published for anyone to use and encrypt messages. However, only the receiving party has access to the decryption key and is capable of reading the encrypted messages.[2] Public-key encryption is a relatively recent invention: historically, all encryption schemes have been symmetric-key (also called private-key) schemes.[1]:478
Encryption has long been used by militaries and governments to facilitate secret communication. It is now commonly used in protecting information within many kinds of civilian systems. For example, the Computer Security Institute reported that in 2007, 71% of companies surveyed utilized encryption for some of their data in transit, and 53% utilized encryption for some of their data in storage.[3] Encryption can be used to protect data "at rest", such as files on computers and storage devices (e.g. USB flash drives). In recent years there have been numerous reports of confidential data such as customers' personal records being exposed through loss or theft of laptops or backup drives. Encrypting such files at rest helps protect them should physical security measures fail. Digital rights management systems which prevent unauthorized use or reproduction of copyrighted material and protect software against reverse engineering (see also copy protection) is another somewhat different example of using encryption on data at rest.
Комментарии:
4,000 square foot GARDEN TOUR! Zone 4 in-ground garden: mid-season tour!
Whole-Fed Homestead
Tasty Ekwang Recipe in Diaspora. No Juicer, No Grater! 4 Wrap Leaves to use!
Cooking With Claudy
One in a Billion Moments in Nature
#Mind Warehouse
Turkcell Reklam Filmi Betigül Ceylan
Betigül Ceylan